This microphone was part of the estate of an amateur journalist. As she moved into treatment and into hospice, there were other concerns besides removing the batteries from unused equipment. Could the Unbrokenstring Crew revive this unit and make it usable again?
 This microphone is a basic SM58 capsule coupled to a battery-operated VHF FM transmitter.
This microphone is a basic SM58 capsule coupled to a battery-operated VHF FM transmitter.
 These are often seen in many performance venues as well as in worship, news-gathering, and business settings.
These are often seen in many performance venues as well as in worship, news-gathering, and business settings.
 The 9v battery has leaked. We will need to disassemble the unit to clean up the mess.
The 9v battery has leaked. We will need to disassemble the unit to clean up the mess.
 These VHF units are on frequency allocations that are shared with other services and may be subject to interference. However, these units work well if you are fortunate enough to be in a part of the country where interference is low.
These VHF units are on frequency allocations that are shared with other services and may be subject to interference. However, these units work well if you are fortunate enough to be in a part of the country where interference is low.
 The microphone capsule is built into the head of the microphone, which unscrews from the electronics. Connections between the capsule and the electronics are reliable regardless of how many turns are necessary to tighten the threaded bodies together.
The microphone capsule is built into the head of the microphone, which unscrews from the electronics. Connections between the capsule and the electronics are reliable regardless of how many turns are necessary to tighten the threaded bodies together.
 The gold fingers touch those rings seen in the previous picture.
The gold fingers touch those rings seen in the previous picture.
 This inside snap ring keeps the electronics inside the housing.
This inside snap ring keeps the electronics inside the housing.
 Before we remove the electronics,we need to get the switch actuators out of the case. The cover removes easily enough.
Before we remove the electronics,we need to get the switch actuators out of the case. The cover removes easily enough.
 The switch actuators come straight out.
The switch actuators come straight out.
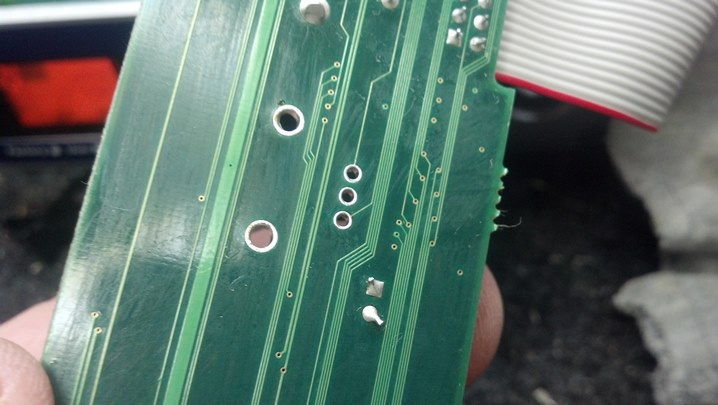
 This is the complete analog FM transmitter.
This is the complete analog FM transmitter.
 Working with the battery contacts is much easier now that the case is out of the way.
Working with the battery contacts is much easier now that the case is out of the way.
 Reassembly is the reverse of disassembly. Wow, that’s profound…
Reassembly is the reverse of disassembly. Wow, that’s profound…
 These big tweezers are all I need to get the inside snap ring back in place.
These big tweezers are all I need to get the inside snap ring back in place.
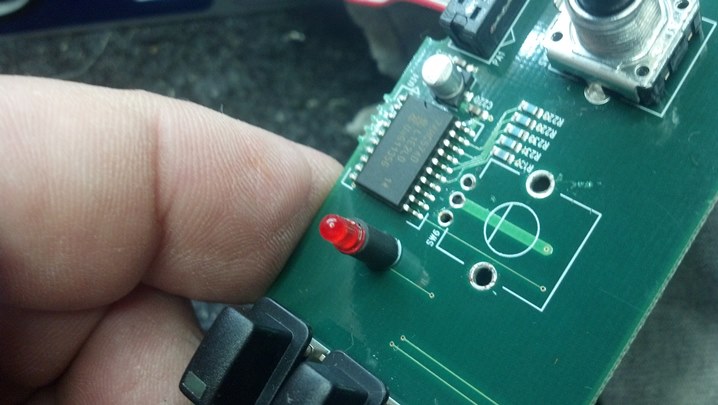
 Reassembled, the new battery is installed and we have a green light!
Reassembled, the new battery is installed and we have a green light!
 The receiver indicates that an FM carrier is present.
The receiver indicates that an FM carrier is present.
 We have an intermittent problem with audio out of the microphone. We need to look at the capsule.
We have an intermittent problem with audio out of the microphone. We need to look at the capsule.
 I guess we’ve screwed the pooch by now.
I guess we’ve screwed the pooch by now.
 The wires are cracked where they emerge from the solder joints. These will be reworked.
The wires are cracked where they emerge from the solder joints. These will be reworked.
 This brass adapter goes between the capsule and the rest of the housing.
This brass adapter goes between the capsule and the rest of the housing.
Thanks for reading all the way to the end!
CONTACT – David Latchaw EE
281-636-8626